Java Identifiers
Java Identifiers
- A name in java program is called identifier, which can be used for identification purpose.
- It can be method name, variable name, class name or label name.
Example
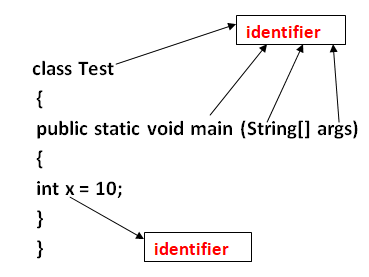
Rules for defining java identifiers:-
- The only allow characters in java is identifer are a to z , A to Z, 0 to 9 , _ and $ . By mistake if you are using any other character you will get compile time error.
example: int total_number = 7; - Identifiers can’t start with digits.
example: int 123total = 25;
example: int total123 = 25; - Java identifier are case sensitive offcourse java language itself is treated as case sensitive programming language.
Example
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 10;
int Number = 20;
int NUMBER = 30;
int NUMber = 40;
}
}
Note:- All variables are different. We can differentiate with case.
- There is no length limit for java identifer but it is not recommended to take too lengthy identifer.
example: int abcdefghijklmnopqrst = 7; - We can’t use reserved words or keyword as identifer.
example: int else = 25; - All predefined java class name and interface name we can use as identifier.
Example
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int String = 888;
System.out.println(String);
}
}
Example
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int Runnable = 888;
System.out.println(Runnable);
}
}
Note:- Even it is valid but it not good a good programming practice because it reduces readability and creates confusion.